- Published on
自平衡二叉树的实现及时间复杂度分析
- Authors

- Name
- 不作声
- GitHub
- Github @buzuosheng
平衡二叉树的实现
我们在遍历二叉树时,先一直往左遍历,于是我们发现,当一棵树的每个节点都只有一个子节点时,他就变成了一个链表,然后链表就说啊:
年轻人你不要过度消费我,这好吗?这不好。
所以我们针对这个问题进行优化,就出现了平衡二叉树。
何为平衡,平衡是指,二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的高度差都不大于1。当插入或删除一个节点时,我们需要通过一次或多次树的旋转来保持二叉树的平衡。
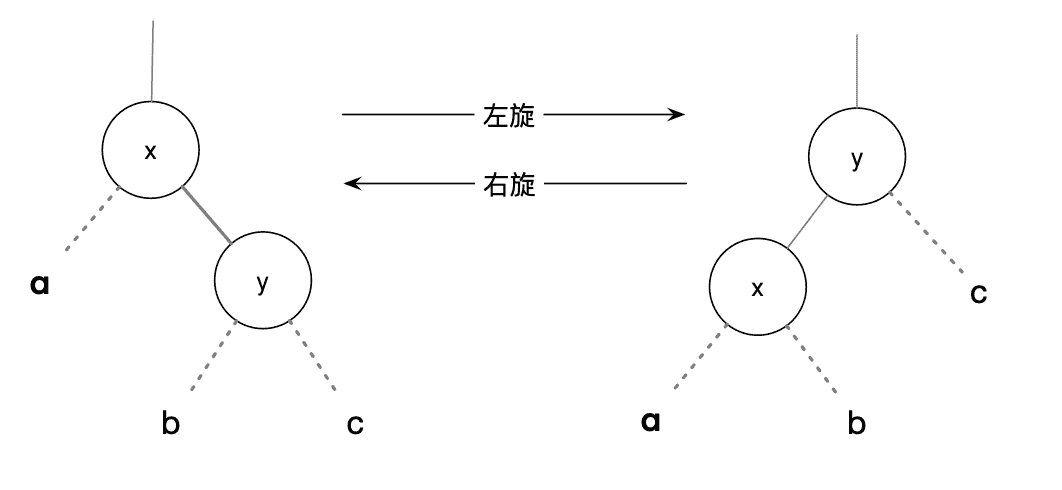
树的旋转分为左旋和右旋两种具体操作,这两种操作是完全相反的,互为逆操作。
左旋是将该节点的右子树逆时针旋转,右旋是将该节点的左子树顺时针旋转。
对于一个节点node进行左旋操作时,具体操作为:将node.right子树取下,node.right节点称为新的根节点newRoot,将node接在newRoot的左节点,newRoot.left取下接在node的右节点上。
右旋操作相反:将node.left子树取下,node.left节点作为新的根节点newRoot,将node接在newRoot的右节点,newRoot.right取下接在node的左节点上。
AVL插入节点有四种情况,分别为左子树左节点,左子树右节点,右子树左节点,右子树右节点。
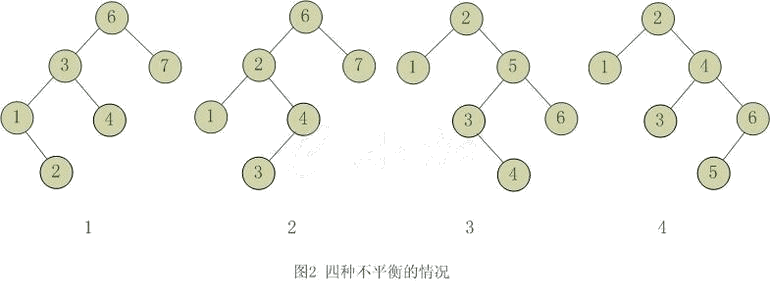
对于左子树左节点,进行一次右旋操作,右子树右节点,进行一次左旋操作可以恢复平衡。
对于左子树右节点和右子树左节点需要两次旋转才能恢复平衡。
代码实现:
// 构造节点,使用节点的height属性判断是否平衡
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
this.height = 1
}
}
class AVL {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
// 获取节点的高度
getHeight(node) {
if(!node) return 0
return node.height
}
// 左旋的具体操作,将node节点的node.right取下,作为新的根节点,node.right.left取下
// 将node接在node.right节点的左节点,node.right.left节点接在node的右节点
leftRotate(node) {
let newRoot = node.right
let newNode = newRoot.left
newRoot.left = node
node.right = newNode
node.height = 1 + Math.max(this.getHeight(node.left),
this.getHeight(node.right))
newRoot.height = 1 + Math.max(this.getHeight(newRoot.left),
this.getHeight(newRoot.right))
return newRoot
}
// 右旋的操作与左旋相反,将上述代码中的left换成right,right换成left就行
rightRotate(node) {
let newRoot = node.left
let newNode = newRoot.right
newRoot.right = node
node.left = newNode
node.height = 1 + Math.max(this.getHeight(node.left),
this.getHeight(node.right))
newRoot.height = 1 + Math.max(this.getHeight(newRoot.left),
this.getHeight(newRoot.right))
return newRoot
}
addNode(value){
this.root = this.addChild(this.root, value)
}
// 平衡因子,判断一个二叉树是否平衡
getBalance(node) {
return this.getBalance(node.left) - this.getBalance(node.right)
}
// 添加一个节点分为四种情况,分别为左子树的左节点,左子树的右节点,右子树的左节点,右子树的右节点。
// 每种情况都要单独处理
addChild(node, value) {
if (!node) return new Node(value)
if (node.value > value) {
node.left = this.addChild(node.left, value)
} else if (node.value, value) {
node.right = this.addChild(node.right, value)
} else {
node.value = value
}
node.height = 1 + Math.max(this.getHeight(node.left), this.getHeight(node.right))
let balance = this.getBalance(node)
// 左子树左节点,左子树高且左子树的左子树高,左子树可能平衡但整体树不平衡
if(balance > 1 && this.getBalance(node.left) >= 0) {
return this.rightRotate(node)
}
// 右子树右节点,右子树高且右子树的右子树高,右子树可能平衡,但整体不平衡
if(balance < 1 && this.getBalance(node.right) <= 0) {
return this.leftRotate(node)
}
// 左子树右节点,左子树高且左子树的右子树高,先左旋再右旋
if(balance > 1 && this.getBalance(node.left) < 0) {
node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left)
return this.rightRotate(node)
}
// 右子树左节点,右子树高且右子树的左子树高,先右旋再左旋
if(balance < 1 && this.getBalance(node.right) > 0) {
node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right)
return this.leftRotate(node)
}
return node
}
}
如果添加一个节点后,树还保持平衡就不做处理直接添加。
添加节点之后就是删除节点。删除节点的操作也是类似的,首先删除节点,如果使用子树替换删除的节点,再判断树是否平衡,再经过一次或多次旋转后使树保持平衡。
时间复杂度分析
对于查找操作而言,二叉搜索树的时间复杂度介于O(log2N)到O(n)之间,如果退化成单链表,时间复杂度就是顺序查找,为O(n)。如果是平衡二叉树,查找效率会提高到O(log2N)。
对于增加节点操作,二叉搜索树增加与查找的复杂度相同,而平衡二叉树在增加节点后,还可能进行额外的旋转操作。
对于删除操作来说,二叉搜索树在查找的基础上可能会多一个最小后继节点替换操作,平衡二叉树还要在这个基础上增加一个可能的一次或多次树的旋转操作。